Mouse anti-NFKB1 Monoclonal Antibody(1298CT792.105.117.133)描述别名宿主特异性反应种属应用分子量类型克隆号同种型储存/保存方法存储溶液研究领域背景说明细胞定位UniProt参考文献
| 概述 | |
| 描述 |
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Mab)
|
| 别名 |
NFKB1抗体;Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit; DNA-binding factor KBF1; EBP-1; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p50 subunit; NFKB1
|
| 宿主 |
Mouse
|
| 特异性 |
This antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein from human NFKB1.
|
| 反应种属 |
Human
|
| 应用 |
FC~~1:25
IHC-P~~1:25 WB~~1:1000 |
| 分子量 |
Predicted molecular weight: 105kD
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors. |
| 性能 | |
| 类型 |
Monoclonal Antibody
|
| 克隆号 |
1298CT792.105.117.133
|
| 同种型 |
IgG1,κ
|
| 储存/保存方法 |
Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long time storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 存储溶液 |
Purified monoclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein G column, eluted with high and low pH buffers and neutralized immediately, followed by dialysis against PBS.
|
| 研究领域 |
Cancer;Cell Biology;Immunology;Signal Transduction
|
| 靶标 | |
| 背景说明 |
NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5′-GGRNNYYCC-3′, located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105.
|
| 细胞定位 |
Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor (I-kappa-B)
|
| UniProt |
P19838
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 参考文献 |
Kieran M.,et al.Cell 62:1007-1018(1990).
Bours V.,et al.Nature 348:76-80(1990). Meyer R.,et al.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:966-970(1991). Heron E.,et al.Genomics 30:493-505(1995). Chang H.-M.,et al.Submitted (DEC-1999) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases. |
实验结果图
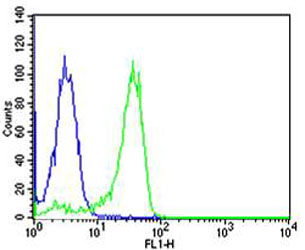
Flow cytometric analysis of Hela cells using NFKB1(green, Cat#JP100408) compared to an isotype control of mouse IgG1(blue). JP100408 was diluted at 1:25 dilution. An Alexa Fluor® 488 goat anti-mouse lgG at 1:400 dilution was used as the secondary antibody.
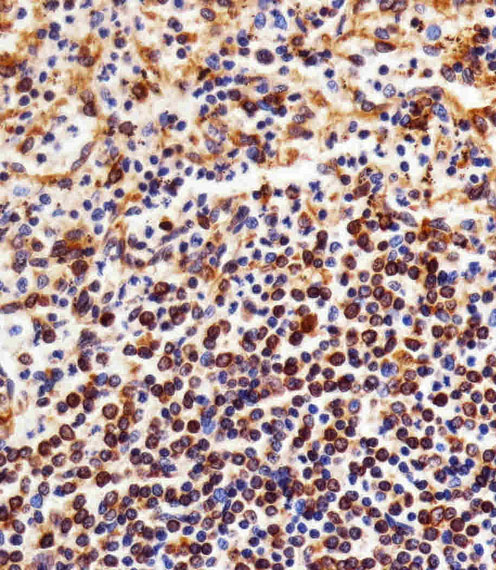
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded H. spleen section using NFKB1(Cat#JP100408). JP100408 was diluted at 1:25 dilution. A peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG at 1:400 dilution was used as the secondary antibody, followed by DAB staining.
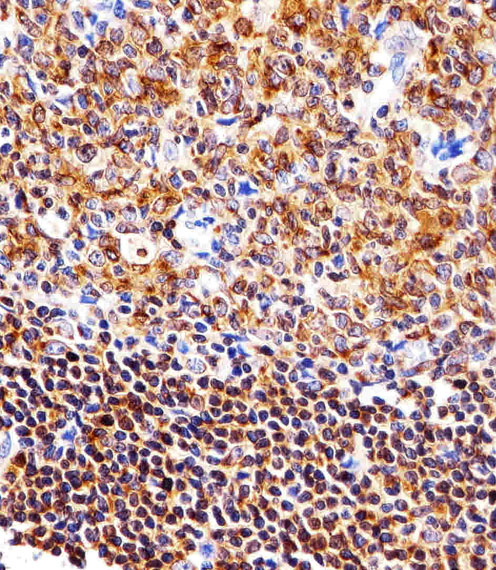
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded H. tonsil section using NFKB1(Cat#JP100408). JP100408 was diluted at 1:25 dilution. A peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG at 1:400 dilution was used as the secondary antibody, followed by DAB staining.
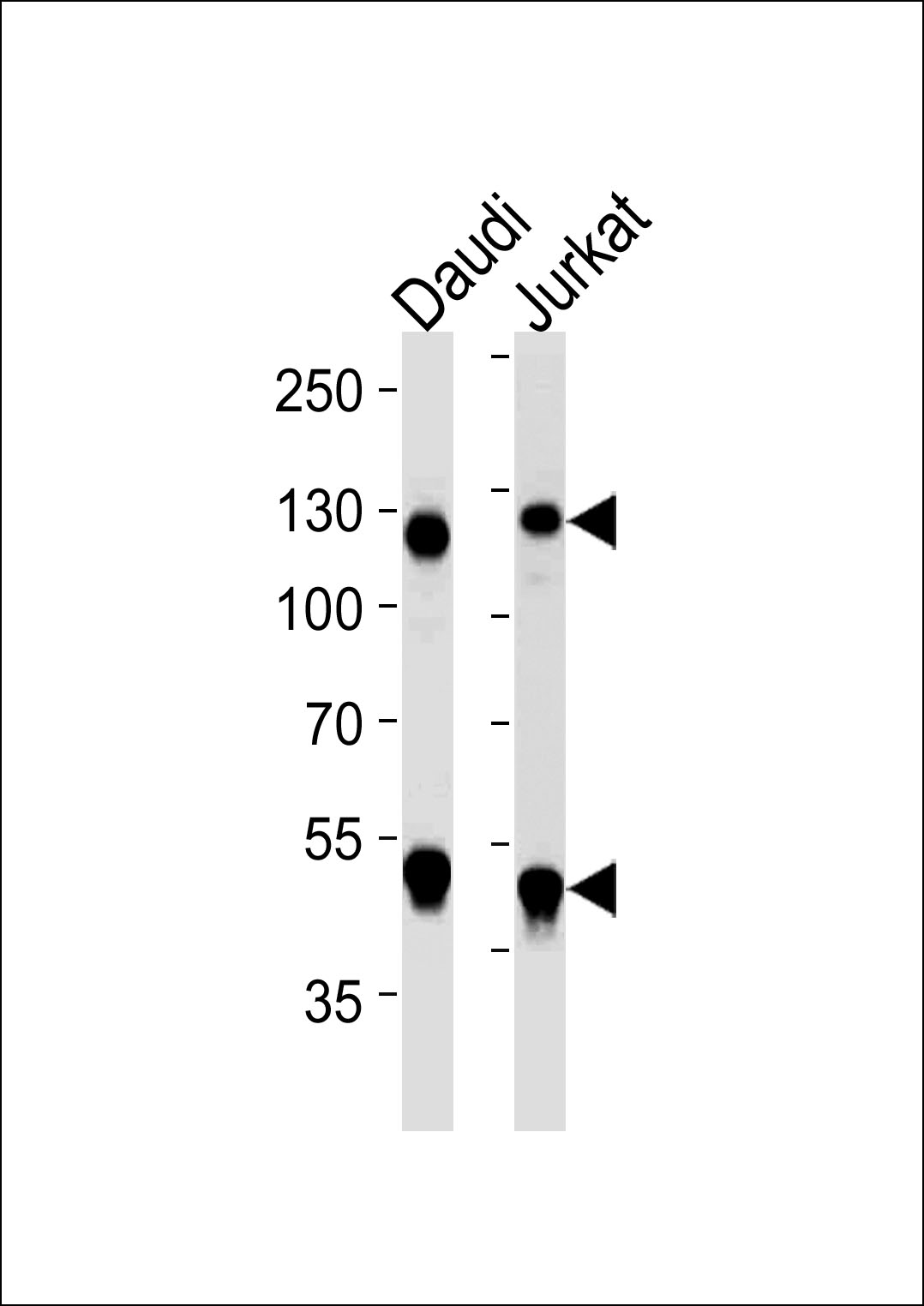
Western blot analysis of lysates from Daudi, Jurkat cell line (from left to right), using NFKB1 Antibody(Cat. #JP100408). JP100408 was diluted at 1:1000 at each lane. A goat anti-mouse IgG H&L(HRP) at 1:5000 dilution was used as the secondary antibody. Lysates at 35μg per lane.
