PNGase F (Peptide-N-Glycosidase F)
肽-N-糖苷酶F
N-Peptide-N4-(acetyl-ß-glucosaminyl)-asparagine amidase; N-Glycosidase F
肽-N4-(乙酰基葡糖胺)-天冬酰胺酶;N-糖苷酶F
来源:脑膜脓毒性伊丽莎白菌(Elizabethkingia meningosepticum)
EC编号: 3.5.1.52
|
Catalog Numbers
|
Size
|
酶活
|
|
E-PNG01
|
60 µl
|
0.3 U
|
|
E-PNG01-20
|
20 µl
|
0.1 U
|
|
E-PNG01-200(E-PNG05)
|
200 µl
|
1.0 U
|
推荐试剂,包含E-PNG01:
1小瓶: 5x 反应缓冲液 pH 7 – 400 µl
1小瓶: 变性溶液 – 200 µl 2% SDS/ 1 M β-巯基乙醇
1小瓶: 15% Triton X-100 – 200 µl
活力: 5 U/ml
比活力: ≥ 25 U/mg
分子量: 大约为35 kD.
最优pH: 7.5, 在 6-10范围具备酶活性。
储存: 比活力
一个单位的肽-N-糖苷酶F活力定义为,在37°C,pH 7.5时在1分钟内从1微摩尔核糖核酸酶B上催化释放N-链接寡糖所需酶的数量。通过SDS-PAGE监测裂解(裂解核糖核酸酶B迁移更快)。
配方:该酶溶于20mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)中,并经无菌过滤。
特异性
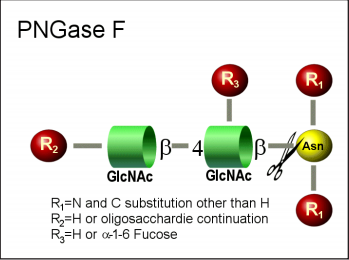
肽-N-糖苷酶F可将天冬酰胺链接(N-链接)寡糖从糖蛋白上裂解下来。肽-N-糖苷酶F使天冬酰胺脱氨基成为天冬氨酸,而寡糖部分则保持完整。
变性使裂解率增加到100倍。大多数天然蛋白质仍然可以完全N-去糖基化,但必须增加培养时间。肽-N-糖苷酶F在培养条件下,可保持活性至少72小时。
肽-N-糖苷酶F不会去除含有α-(1,3)键核心稳定性:
在室温条件即使曝露几天,也不会使活力下降。如果储存得当,可至少稳定12个月。
质量和纯度
肽-N-糖苷酶F的蛋白酶污染检测过程如下: 将10μg变性BSA与2μl酶在37°C下培养24小时。SDS-PAGE a分析显示处理后的BSA没有退化迹象。
通过延长与相应的PNP糖蛋白一起培养的时间,可以确认外糖苷酶污染物是否存在。肽-N-糖苷酶F是从伊丽莎白(金杆菌或黄杆菌)脑膜败血症培养上清液中分离出来的。重要的污染物包括内切糖苷酶F,它使部分N-链接的寡糖在二乙酰壳二糖核心结构内发生裂解,留下N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖残基连在天冬酰胺上。这些污染物通过色谱法,从肽-N-糖苷酶F试剂中去除。
使用指导
1. 将至多200µg糖蛋白加入一个Eppendorf离心管中。用去离子水定容到35 µli。
2. 将10 µl 5倍 反应缓冲液(pH7.5)和2.5 µl变性溶液,加热到100°C保温 5分钟。
3. 冷却。加入2.5 µl Triton X-100并混合。
注意:不加Triton X-100会导致肽-N-糖苷酶F活力下降3倍。
4. 往反应溶液中加2.0 µl肽-N-糖苷酶F。在37°C下培养3小时。 如省略了SDS或热变性,那么培养时间应增加到至少24小时。 通过SDS-PAGE来监控裂解反应。
参考文献:
Bayer, E.A., F. De Meester, T. Kulik and M. Wilchek. Preparation of deglycosylated egg white avidin. Appl Biochem Biotech 53: 1-9 (1995)
Elder, J.H. and S . Alexander. endo-b-N-Acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 4540-4544 (1982)
Tarentino, A .L. , C.M. Gomez an d T.H . Plummer, Jr. Deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans by peptide:N-glycosidase F . Biochemistry 24: 4665-4671 (1985)
Tarentino A.L. and T.H. Plummer. Enzymatic deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans: purification, properties, and specificity of oligosaccharide-cleaving enzymes from Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Meth Enzymol 230:44-57 (1994)
Trimble R.B. and A.L. Tarentino. Identification of distinct endoglycosidase (endo) activities in Flavobacterium meningosepticum: endo F1 , endo F2 and endo F3. Endo F1 and endo H hydrolyze only high mannose and hybrid glycans. J Biol Chem 266:1646-1651 (1991).
Taga, E. M., A. Waheed and R. L. Van Etten. Structural and chemical characterization of a homogeneous peptide N-glycosidase from almond. Biochemistry 23:815-22 (1984).